The Definitive Guide to SAP Certification: Navigating Your Path to Expertise and Career Advancement
A comprehensive overview of SAP certification, a globally recognized credential vital for professionals and organizations navigating the evolving landscape of enterprise resource planning (ERP) and business technology. It delves into the strategic importance of SAP certification for individual career growth and organizational efficacy, details the diverse certification landscape, outlines the structured process for obtaining and maintaining these credentials, and offers strategic considerations for maximizing their value. The information presented herein aims to equip stakeholders with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions regarding SAP skill development and validation.
1. Introduction to SAP Certification
This introductory section defines SAP certification, elucidates its core purpose, and underscores its global recognition as a benchmark for expertise in SAP solutions. Understanding these foundational elements is crucial for appreciating the strategic value of SAP credentials in the modern enterprise software ecosystem.

1.1 What is SAP Certification?
SAP certification is formally defined as a globally recognized credential that validates an individual's knowledge and proficiency in Systems, Applications, and Products in data processing.
This program is tailored for professionals seeking to enhance their knowledge and practical skills in SAP technologies, providing a structured pathway to demonstrate competence.

The value of SAP certification extends significantly beyond individual career benefits, offering substantial strategic advantages for organizations. In a competitive market, a certified talent pool ensures higher quality implementations, reduced project risks, optimized system performance, and a stronger competitive edge. This represents a mutual investment in skill and success.
Benefits for Individuals
Obtaining an SAP certification can significantly open doors to professional opportunities, including promotions and new job offers.
A tangible benefit of SAP certification is the potential for higher earnings. Certified professionals generally command higher salaries compared to their non-certified peers, with industry reports indicating better compensation due to their specialized expertise, skills, and potential, making them highly desirable in both government and private sectors.
Certification serves as a robust validation of an individual's knowledge and proficiency in specific SAP skills.
By positioning oneself as an essential asset to organizations relying on SAP software, certification leads to better job stability and long-term career security.
 .
.
Benefits for Organizations
An organization's credibility is significantly boosted when its employees hold validated SAP skillsets.
SAP certifications are instrumental in driving business transformation and accelerating technology adoption within an organization, ultimately leading to maximized return on investment (ROI) from SAP solutions.
A fundamental shift has occurred in how SAP defines and validates competence. While certification has always provided proof of competence, the introduction of continuous skill updates and assessments, particularly the explicit requirement as of April 2024 for yearly assessments to maintain validity
This evolution is intrinsically linked to SAP's strategic direction. The explicit statement that "With SAP's growing focus on SAP S/4HANA, Rise with SAP, and cloud solutions, the certification process needed to reflect modern deployment models"
latest versions of their software, particularly the cloud-based and S/4HANA offerings. This directly supports SAP's core business model, which increasingly relies on cloud subscriptions and widespread adoption of its most current solutions. The emphasis on "RISE with SAP S/4HANA Cloud (public) implementation" certifications further reinforces this strategic alignment.

2. Exploring the SAP Certification Landscape
This section categorizes the various SAP certifications by level and module, providing a structured understanding of the extensive offerings and the progression of expertise within the SAP ecosystem.

2.1 Understanding Certification Levels
SAP offers a comprehensive range of certifications across numerous subjects, systematically categorized into four distinct levels, each representing increasing difficulty and depth of expertise: Associate, Delta, Specialist, and Professional.
Associate Certification: This is the foundational and most common introductory level, designed for individuals beginning their journey in SAP.
Specialist Certification: This level delves deeper into specific roles or integration components within the SAP landscape.
Professional Certification: This is the highest level, tailored for advanced professionals who possess a detailed and comprehensive understanding of SAP solutions, coupled with proven project experience or extensive business process knowledge.
Delta Certification: While not always listed as a standalone "level" in the same vein as Associate, Specialist, or Professional, "Delta" certifications appear in specific contexts, such as "SAP Certified Application Specialist – SAP BW/4HANA 2.0 Delta".
2.2 Key Certification Modules and Domains
SAP offers hundreds of certifications spanning a vast portfolio of solutions, reflecting its comprehensive coverage of enterprise functions.
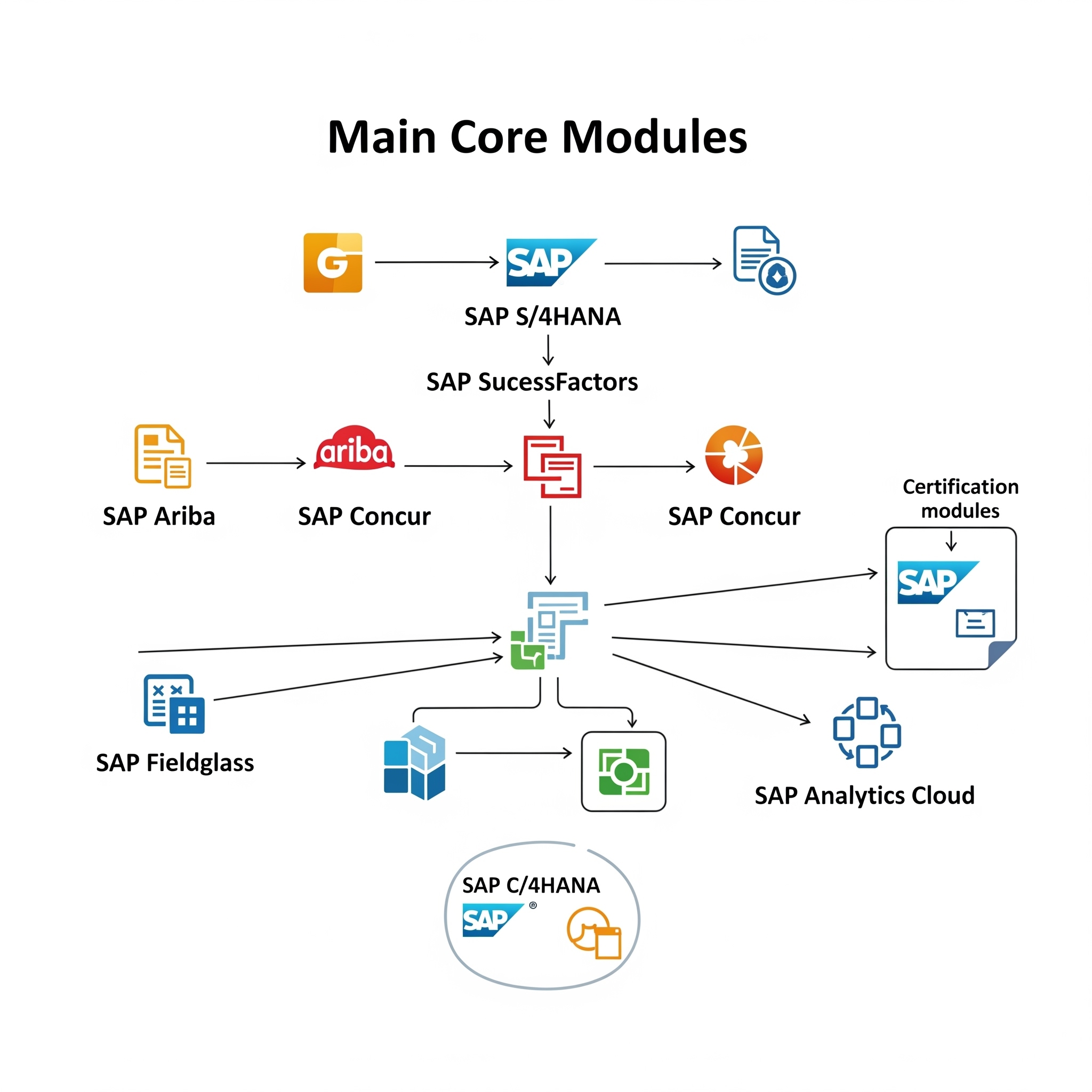
A significant trend observed is SAP's deliberate and strategic pivot towards its cloud-first solutions and a more granular, practical approach to skill validation. The explicit statement that "SAP has moved towards role-specific certifications (e.g., SAP S/4HANA Finance Consultant, SAP Analytics Cloud Specialist) rather than generic module-based ones"
Another important aspect is the interconnectedness and prerequisite structure within the certification program. The explicit inclusion of prerequisites and recommended prior certifications
The following table provides a concise overview of key SAP certification modules and example certifications by level:
Table 1: Overview of Key SAP Certification Modules and Example Certifications by Level
Module/Domain | Example Certification Name | Certification Level | Brief Description/Key Skills Validated |
SAP Activate Methodology | SAP Certified Associate – SAP Activate Project Manager | Associate | Ability to use SAP Activate Methodology for S/4HANA implementations |
SAP Certified Specialist – SAP Activate for Cloud Solutions Project Manager | Specialist | Understanding of advanced business and communication skills for cloud projects | |
ABAP and SAP HANA | SAP Certified Technology Associate – SAP HANA 2.0 | Associate | Readiness to be an SAP HANA technology consultant with basic knowledge and project experience |
SAP Certified Development Specialist – ABAP for SAP HANA 2.0 | Specialist | Ability to use ABAP for SAP HANA programming knowledge for development consultant role | |
SAP Certified Development Associate – ABAP with SAP NetWeaver 7.5 | Associate | Foundational knowledge in ABAP Development, requiring expert supervision | |
Financials (FICO) | SAP Certified Application Associate – SAP S/4HANA for Financial Accounting Associates | Associate | Knowledge in financial closing, general ledger accounting, accounts payable/receivable, asset accounting |
SAP Certified Application Professional – Financials in SAP S/4HANA for SAP ERP Finance Experts | Professional | Skills to independently prepare, set up, and lead S/4HANA Financials implementation projects | |
Supply Chain Management (SCM) | SAP Certified Application Associate – SAP S/4HANA Sourcing and Procurement | Associate | Knowledge in sourcing and procurement processes within S/4HANA |
SAP Certified Application Associate – Extended Warehouse Management with SAP S/4HANA | Associate | Understanding of warehouse management for work under a mentor | |
Human Capital Management (HCM) | SAP Certified Application Associate – SAP HCM Payroll with ERP 6.0 | Associate | Basic knowledge of SAP Payroll, including rules, wage types, and integration |
SAP Certified Application Associate – SAP SuccessFactors Recruiting: Recruiter Experience 2H/2021 | Associate | Ability to implement SAP SuccessFactors Recruiting application | |
Business Intelligence & Analytics | SAP Certified Application Associate – SAP BusinessObjects Business Intelligence Platform 2.0 | Associate | Skills to use SAP BusinessObjects BI platform, support users, and configure servers |
SAP Certified Application Specialist – SAP BW/4HANA 2.0 Delta | Specialist | Readiness as an SAP BW Application Consultant with knowledge in BW/4HANA implementation and modeling | |
SAP S/4HANA Cloud (Public) Implementation | SAP Certified Application Associate – SAP S/4HANA Cloud (public) – Service Implementation | Associate | Knowledge of SAP Activate onboarding and Service line of business for cloud implementation |
SAP Ariba | SAP Certified Application Associate – SAP Ariba Sourcing | Associate | Knowledge for an SAP Ariba Sourcing Associate Application Consultant role |
SAP Certified Application Associate – SAP Ariba Procurement | Associate | Understanding of the SAP Ariba Procurement application fundamentals | |
SAP System Security | SAP Certified Technology Professional – System Security Architect | Professional | Qualifies for an SAP Security Architect role with years of experience in system security and authorization |
Other Specific Certifications | SAP Certified Associate – Design Thinking | Associate | Knowledge in SAP Design Thinking methodology, processes, workshop organization, and facilitation |
SAP Certified Application Associate – SAP Business One Release 10.0 | Associate | Experience in implementation, logistics, financials, and support for Business One |
Note: This table provides a representative selection; SAP offers hundreds of certifications across its vast portfolio.
3. The Certification Journey: Process and Preparation
This section details the step-by-step process of obtaining an SAP certification, including comprehensive information on official SAP training resources and the recommended experience levels for each certification tier. The certification process is meticulously designed to be both accessible and rigorous, ensuring that all certified professionals meet SAP's high standards of competence. The recent evolution towards a subscription-based model, particularly through the SAP Learning Hub, underscores SAP's strategic emphasis on continuous learning and the rapid adoption of its cloud solutions. This structured approach aims to streamline the certification journey while maintaining its integrity.

3.1 Step-by-Step Guide to Obtaining Certification
The journey to becoming SAP certified follows a structured and systematic process, designed to guide candidates effectively
Choose Your Certification: The initial and most critical step involves identifying a certification that is precisely tailored to career goals, current skill level, and specific SAP expertise.
Prepare for Your Exam: Once a certification is chosen, candidates must follow dedicated learning journeys to build the necessary skills in the latest SAP solutions.
Purchase a Subscription or Exam Attempts: SAP offers various purchasing options to access exams and learning materials:
SAP Learning Hub Subscription: This is the most comprehensive option, providing access to all resources required to prepare for, take, and crucially, maintain certifications.
Individual Exam Attempts: Candidates can also purchase standalone exam attempts. Options include one, two (which come with 10 hours of certification-relevant hands-on practice system access), or six exam attempts.
do not include access to the assessments required for staying certified annually.
Schedule an SAP Certification Exam: Upon receiving confirmation of a purchased subscription or exam attempts, individuals will be able to schedule their SAP Certification exam. This is typically done via the SAP Learning site, which provides a single sign-on into the Certification Hub.
Access the Exam Dashboard: After scheduling, candidates are directed to the Certification Hub's Exam Dashboard, where they can conveniently view their exam results and monitor any remaining attempts within their subscription.
Select the Right Certification for Scheduling: Within the Certification Hub, candidates review the available exams from a menu and click a blue calendar icon to schedule their chosen exam.
Find a Suitable Exam Date and Time: Candidates must carefully select a suitable date and time, ensuring the correct time zone is chosen before saving the appointment.
Reschedule (if necessary): If a candidate needs to reschedule an exam, they must first delete the existing appointment and then follow the process to set up a new one.
Receive Confirmation Email: Following a successful appointment scheduling, a confirmation email will be sent from
donotreply@examity.com. Candidates are advised to review this email carefully for accuracy and contact SAP support if any details are incorrect.
3.2 Official SAP Training Resources
SAP provides a robust and diverse ecosystem of official learning tools, recognizing that different learners have varying needs and preferences. These resources are crucial for effective preparation and continuous skill development.

SAP Learning Hub: Positioned as the leading digital learning platform, SAP Learning Hub is designed to help individuals and teams rapidly build, enhance, and maintain essential SAP skills.
SAP Learning Class: SAP Learning Class offers structured, instructor-led courses that are available both onsite and online.
Additional Learning Resources: Beyond the core Learning Hub and Learning Class offerings, SAP provides other valuable resources:
Developer Tutorials: Hundreds of tutorials with step-by-step instructions for building applications and learning about product capabilities.
Product Road Maps: Provide an up-to-date overview of planned and available innovations for the SAP software portfolio.
SAP Support Portal: A destination to search knowledge bases, find solutions to issues, and report incidents.
SAP PRESS Certification Success Guides: Books directly relating to specific certification exams, often written by authors who have passed the exams.
Free Tier Trials: Opportunities to gain hands-on experience with SAP solutions like SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP) and S/4HANA Cloud.
SAP Community Forums: Platforms like SAP Community and Reddit offer opportunities for knowledge exchange and discussions among peers.
3.3 Prerequisites and Recommended Experience for Each Level
The SAP certification program incorporates prerequisites and recommended experience levels to ensure candidates possess the foundational knowledge necessary for success at each tier, maintaining the integrity and value of the credentials. This tiered prerequisite structure is fundamental to the SAP certification program. It ensures that candidates build their expertise progressively, mastering foundational concepts before moving on to more complex and specialized areas. This approach not only maintains the credibility of the certifications but also guides individuals on a logical and effective learning progression, mirroring the real-world demands of SAP implementation and management roles.
Associate Level: Generally, introductory associate exams, such as the "SAP Activate Project Manager" exam, do not have explicit prerequisites or prior requirements for registration through the SAP site.
not a prerequisite, making it suitable for professionals with less than 3 years of experience in the field.
Specialist Level: Certifications at the specialist level frequently recommend or require prior associate-level certifications to ensure a solid knowledge base. For example, "SAP Certified Development Specialist – ABAP for SAP HANA 2.0" strongly encourages passing "SAP Certified Development Associate – ABAP with SAP NetWeaver" before attempting the exam.
Professional Level: These certifications demand a higher level of expertise, explicitly requiring prior project experience and in-depth knowledge of SAP solutions.
A significant shift in SAP's approach to certification preparation and assessment is the strategic imperative of hands-on practice and "real-world" application. The SAP Learning Hub offers "unlimited hands-on learning via SAP Live Access" and "preconfigured practice systems".
Another critical consideration is the cost-benefit analysis of SAP Learning Hub for continuous certification and ecosystem engagement. SAP Learning Hub subscriptions include four exam attempts per year and are described as the "simplest path to staying certified" via mandatory yearly assessments.
not include these crucial stay-current assessments.
mandatory yearly assessments for maintaining certification validity
4. SAP Certification Exam Details
This section provides specific and comprehensive information about the format, structure, and secure environment of SAP certification exams, crucial details for any prospective candidate.
4.1 Exam Format and Structure
SAP certification exams typically adhere to a standardized format, though variations exist depending on the specific certification and its level. Understanding the precise exam format and scoring rules is paramount for effective preparation. The evolution towards more practical and scenario-based questions in newer exams directly reflects SAP's strategic emphasis on validating real-world applicability of skills, ensuring that certified professionals are not just theoretically knowledgeable but also practically capable.
Most certification exams for SAP are up to three hours in duration.
The primary question types are multiple choice and multiple selection.
all correct answers for a question to be considered correctly answered; partial credit is not awarded.
Regarding scoring, there is no penalty for incorrect answers, meaning incorrect answers will not detract from the overall score. Therefore, it is strongly advised to answer every question, even if it's an educated guess.
4.2 Exam Environment and Security
To ensure the integrity and credibility of its certifications, SAP employs stringent measures for its exam environment, whether taken remotely or at a testing center. This approach reflects SAP's commitment to balancing accessibility with the critical need to maintain the integrity and value of its certification program. These measures are a direct response to the evolving landscape of online testing and the imperative to protect the brand value of an SAP certification in a global market.
Candidates have the flexibility to take SAP certification exams either at an authorized certification center or conveniently online via remote proctoring.
A significant benefit for candidates is that results are provided immediately upon submitting their finalized answers, whether the exam is taken online or at a physical center.
The tension between maximizing accessibility (online delivery, flexible scheduling) and maintaining the prestige and trustworthiness of the certification (preventing fraud) is a critical challenge for all high-stakes IT certifications. SAP's significant investment in AI monitoring and rigorous proctoring protocols
The transition from traditional paper certificates to dynamic digital badges
Conclusions
SAP certification stands as a cornerstone for validating expertise in the dynamic realm of enterprise software. Its value proposition is dual-faceted, offering significant career advancement and earning potential for individuals, while simultaneously enhancing organizational credibility, operational efficiency, and the ability to drive successful business transformations. The program's evolution, particularly its shift towards continuous validation via annual assessments and a focus on role-based, cloud-centric certifications, reflects SAP's strategic imperative to align its workforce with the latest innovations, especially S/4HANA and cloud solutions.
The tiered structure of Associate, Specialist, Professional, and Delta certifications provides a clear pathway for skill development, emphasizing the interconnected and complex nature of SAP systems. This progression necessitates a commitment to practical application and hands-on experience, a requirement increasingly integrated into the certification process itself. The SAP Learning Hub emerges as the primary, most cost-effective, and strategically aligned resource for both initial certification and ongoing skill maintenance, fostering continuous engagement with SAP's learning ecosystem.
Finally, the rigorous yet flexible exam environment, coupled with the adoption of digital badges, underscores SAP's dedication to maintaining the integrity and market value of its certifications. These measures ensure that an SAP credential remains a globally recognized symbol of excellence, providing verifiable proof of a professional's up-to-date capabilities. For any individual or organization deeply invested in SAP technologies, pursuing and maintaining these certifications is not merely an option but a critical strategic imperative for sustained success and competitive advantage.




